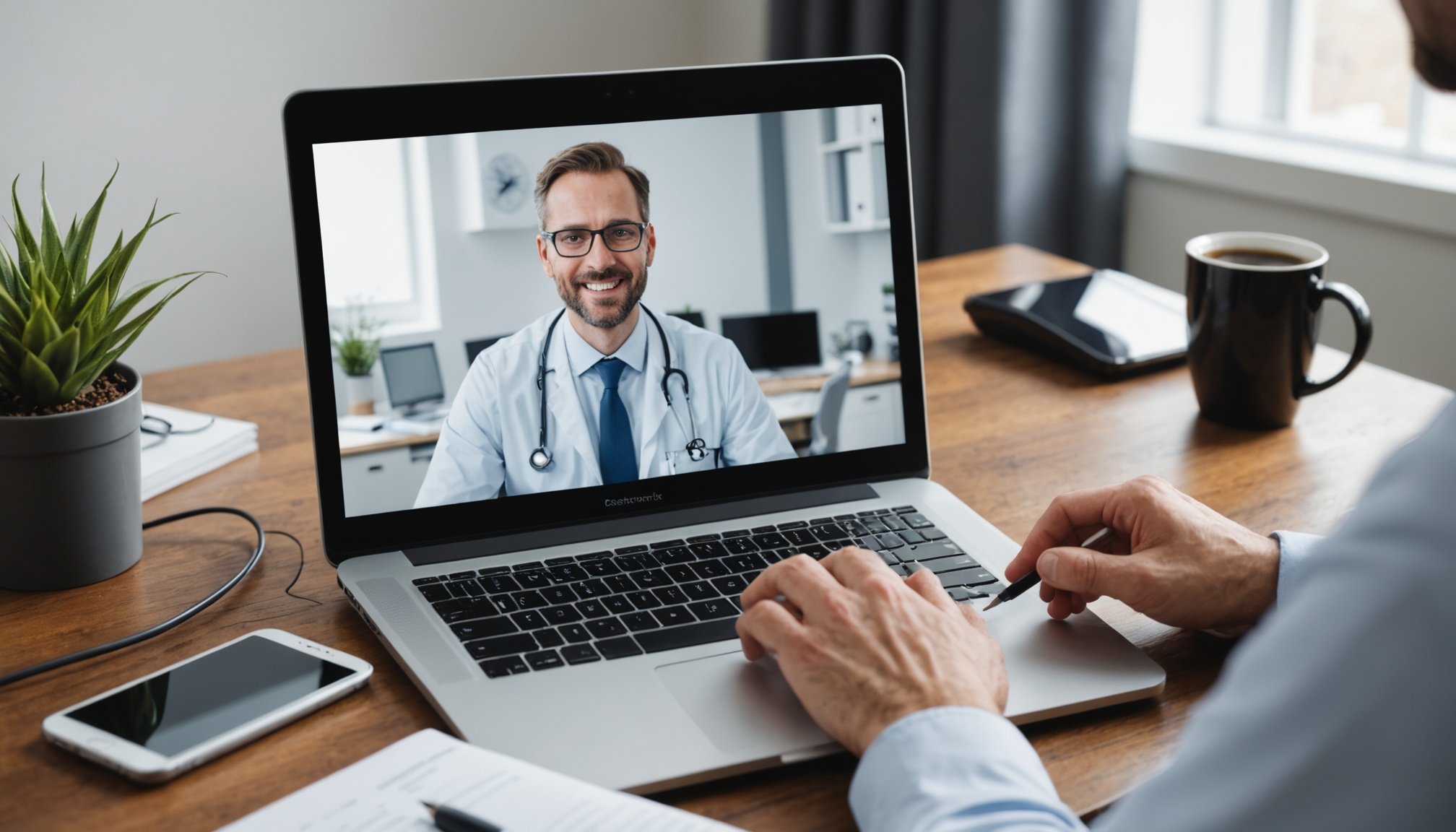
Overview of Telehealth Regulations in the UK
Exploring telehealth regulations within the UK involves understanding the extensive legal framework that governs telehealth services. As telemedicine becomes increasingly prevalent, UK healthcare laws ensure that these services are delivered safely and effectively. The involvement of key regulatory bodies is crucial in maintaining compliance and upholding standards across telehealth platforms.
In the UK, telemedicine compliance is overseen by several important regulatory bodies. These include the Care Quality Commission (CQC), which monitors and inspects health and social care services, and the General Medical Council (GMC), which sets the standards for medical practice. Each body plays a pivotal role in telehealth oversight, ensuring that healthcare services maintain the necessary professional standards and patient safety protocols.
Also to discover : Essential Legal Strategies for UK Businesses: Navigating the 2015 Construction (Design and Management) Regulations with Confidence
Recent trends in telehealth policy changes reflect a rapid evolution in the way health services are delivered. This shift has been accelerated by technological advancements and a growing demand for more flexible healthcare options. Policy adjustments are continuously reshaping the landscape to include integrated technologies while safeguarding patient rights and service quality. Understanding these trends is essential for telehealth providers striving to remain compliant and competitive in the dynamic healthcare environment.
The convergence of technology with healthcare promises an intriguing future, contingent on coherent policy evolution.
Also to see : Mastering the Equality Act 2010: Essential Legal Duties Every UK Business Needs to Understand
Data Protection and Privacy Considerations
The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) significantly shapes telehealth services in the UK, demanding stringent data protection and patient confidentiality measures. This regulation ensures that patient information is processed transparently and securely, essential for maintaining trust in telehealth platforms. GDPR compliance mandates telehealth providers implement robust practices to safeguard data, including encryption and regular audits.
It’s crucial for telehealth services to adhere to these data protection laws, as breaches can lead to severe penalties, including substantial fines and reputational damage. Key practices to uphold patient confidentiality include:
- Implementing strong authentication protocols.
- Ensuring encrypted communication channels.
- Conducting regular security assessments.
Non-compliance with GDPR can result in legal consequences, emphasising the need for telehealth providers to invest in effective data protection strategies.
By prioritising GDPR compliance, telehealth providers not only protect sensitive patient data but also bolster confidence among users, thus contributing to the sector’s growth and acceptance. As the digital healthcare landscape evolves, so too will data protection frameworks, necessitating continuous adaptation and vigilance from providers to align with emerging standards. Staying abreast of these developments is vital for ongoing success and legal security in telehealth.
Licensing and Professional Registration
In the world of telehealth, securing the appropriate healthcare licenses is crucial. Telehealth providers in the UK must adhere to stringent regulations to ensure their services meet legal and ethical standards. Professional registration is a key aspect, where practitioners are required to register with governing bodies like the General Medical Council (GMC) or the Nursing and Midwifery Council (NMC).
Ensuring telehealth practitioners hold valid credentials is paramount. Verifying qualifications and professional registration safeguards patient safety and ensures the delivery of quality healthcare. Telehealth businesses should implement thorough verification processes before service commencement.
Navigating the licensing process can be challenging for telehealth enterprises. An understanding of specific requirements for different healthcare licenses is fundamental. This includes engaging with various health regulatory bodies dependent upon the nature and scope of services offered.
Providers must remain informed about any changes in regulations which may affect existing licenses. This ongoing compliance is crucial for operational continuity and avoiding legal pitfalls. It’s advisable for businesses to consult with legal experts in healthcare regulations to streamline the licensing process and ensure full compliance with UK healthcare laws. This proactive approach diminishes the risk of liabilities and enhances trust with clients.
Informed Consent for Telehealth Services
In the realm of telehealth, informed consent plays a crucial role in safeguarding patient rights. It involves thoroughly explaining the scope of services, potential risks, and benefits to patients before commencing any telehealth interaction. This process is essential to ensure that patients make independent, educated decisions about their healthcare.
Patient rights within telehealth settings entail informing them about how consultations are conducted, data privacy measures, and how follow-up care is managed. Understanding these aspects empowers patients to engage confidently with digital health services.
Telehealth documentation of consent must be meticulous. It involves recording patients’ acknowledgment and agreement to the terms of service, ensuring that they fully comprehend and consent to the treatment provided virtually.
Legal implications arise if informed consent is not properly secured. Without it, telehealth providers may face accusations of negligence or malpractice, leading to disputes and penalties. Therefore, providers must employ best practices for obtaining and archiving consent, such as clear communication and digital consent forms.
By prioritising these practices, telehealth providers uphold ethical standards, foster trust, and mitigate potential legal challenges in their operations. This dedication to transparency and compliance with health regulations protects both patients and healthcare professionals.
Emerging Trends and Legal Developments
In the dynamic world of telehealth, staying current with telehealth trends and legal developments is vital for providers. Recent technological advancements have significantly impacted healthcare innovation, introducing new paradigms in service delivery. The shift towards more integrated and efficient digital health solutions prompts continual adjustments in legal frameworks.
Legal developments in telehealth aim to incorporate emerging technologies while assuring patient safety and service quality. For instance, recent legislative updates have focused on improving data interoperability, ensuring seamless integration across various healthcare platforms. These changes enhance patient management and foster a more cohesive healthcare environment.
Looking ahead, the future of telehealth legislation in the UK pivots around adapting laws to accommodate innovations like artificial intelligence and machine learning in healthcare settings. Legislators and regulatory bodies aim to strike a balance between encouraging technological adoption and maintaining rigorous standards for patient care and ethical practice.
Providers must remain vigilant and informed about these evolving legal landscapes. Engaging with industry updates and participating in professional networks can offer insights into new policies and best practice implementations. This proactive approach is crucial for businesses to navigate potential risks and leverage opportunities arising from ongoing healthcare innovation.
Case Studies on Legal Challenges in Telehealth
Telehealth case studies offer valuable insights into the legal hurdles that UK telemedicine companies often encounter. Take, for instance, the significant legal challenges faced by some providers due to inadvertent breaches of data protection laws. These have highlighted the necessity for robust compliance mechanisms, especially concerning GDPR regulations.
One illustrative case involves a telehealth provider who was penalised for insufficient patient confidentiality measures, underscoring the importance of ensuring airtight security practices. The lessons from such cases emphasise implementing stringent protocols for GDPR compliance and healthcare innovation integration.
Businesses can mitigate legal risks by learning from these case studies. A proactive approach involves regularly reviewing and updating security frameworks to align with evolving UK telemedicine standards and regulations. Engaging with legal experts to audit practices can preempt potential disputes.
Moreover, telehealth enterprises must also focus on patient rights, ensuring transparent communication and securing informed consent. This approach not only helps in addressing legal challenges but also builds trust with users, thereby fostering a more sustainable and ethical telehealth environment. As technology and legal landscapes evolve, such vigilance becomes indispensable.